Model Glider
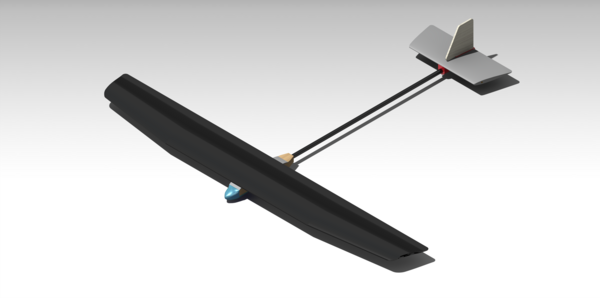
As part of my undergraduate Materials & Manufacturing course (AER507), the end of semester project was to design a model glider including all manufacturing processes. Due to pandemic restrictions, this project was done remotely instead whereas in a normal year the gliders would be built, assembled, and flown on campus. Constraints on the design included a maximum mass of 200 g, a restricted set of available materials, a maximum length and width, a predefined wing shape, and the requirement that the wing be made of a composite material. The goal of the project was to minimize the glider weight within reason, while ensuring that the glider is still easily manufacturable. My role on the team was to design the glider and perform analysis on the wing design. This analysis would later be used to select appropriate materials for the wing.
We selected a hollow design with ribs for our wing, with the main controllable variable being the thickness of the skin. Given the low span loading, the aerodynamic loading wouldn't be the limiting factor until the skin became unreasonably thin. The final wing design included ribs to help withstand the shear loads associated with handling, and uncontrolled landings of the craft.
The fuselage was designed in four components, a foam nose, a wing mount, a wooden core, and a tail boom. The nose is designed to provide a more aerodynamic shape to the wing while also reducing the risk of causing damage to the floor or glider during its uncontrolled landings. The wing mount provides a simple to manufacture method of joining the wing and body. Made of wire cut Depron, it is quick to produce the complex curve to match the lower surface of the wing. The core of the fuselage was constructed from laminated sheets of balsa wood to ensure that it would withstand the moment caused by handling and the aerodynamic forces on the tail. The tail boom is a hollow carbon fiber tube attaching the main body to the tail of the glider.
The tail of the glider features a 3D printed core, a wire cut Depron foam horizontal stabilizer, and a vertical stabilizer. 3D printing was selected to realize the complex shape of the core inexpensively at low volumes. The NACA 0010 stabilizer was made of foam to reduce weight, with a skewer near the leading edge to enhance its rigidity. The vertical stabilizer was made of Lite Ply due to it's high specific stiffness and reduced weight.